Projects
Websites

JWST: The Early Years
Prior to September 10, 2002, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) was known as the Next Generation Space Telescope (NGST). Read about the early history of JWST.
Movies
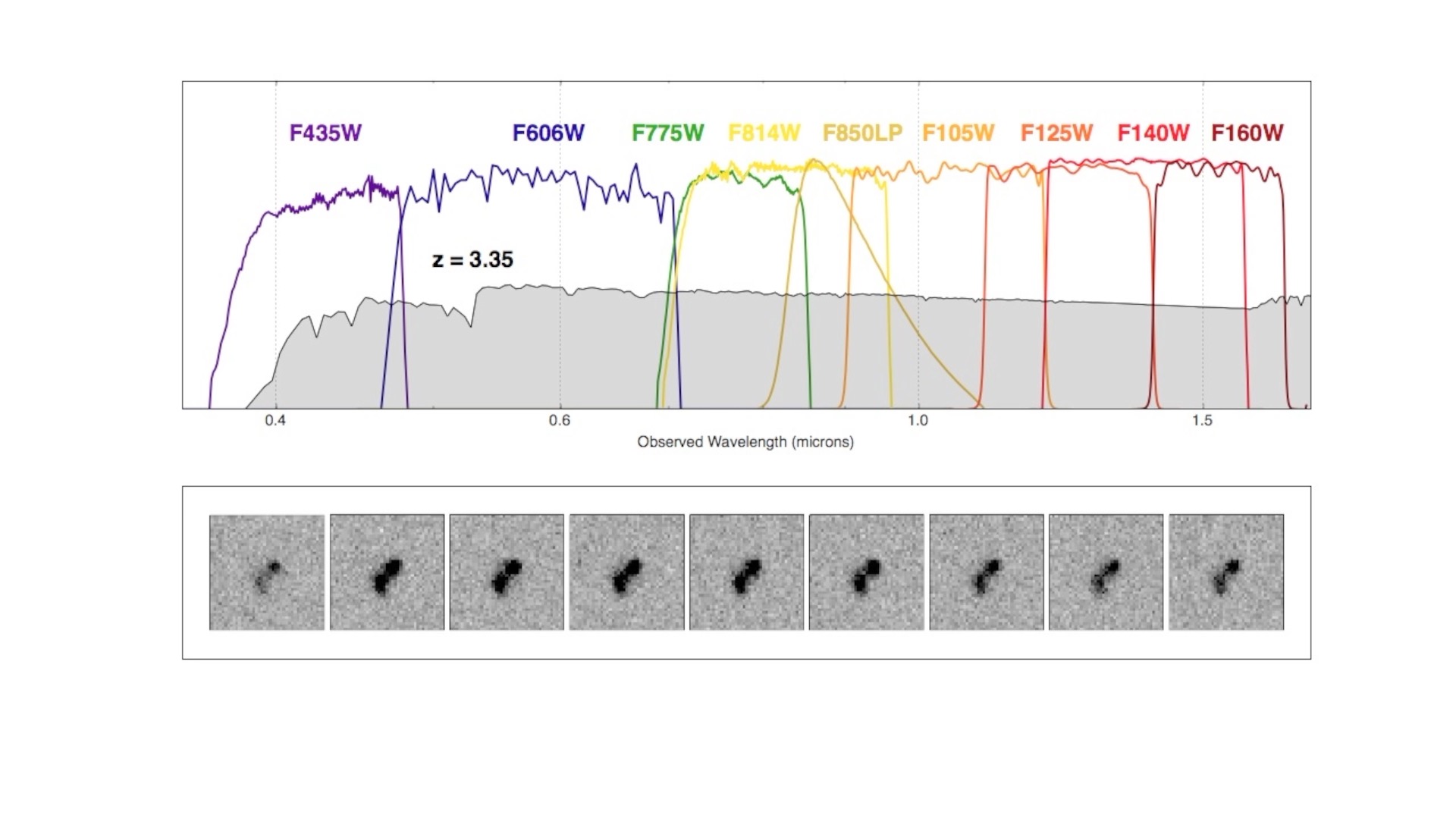
Redshift Movie
A short movie showing how the observed spectrum of star-forming galaxies changes as we observe it at higher and higher redshift. Redshift is denoted here in this movie as "z". Note how the break in the spectrum shifts to redder and redder wavelengths as a result of this redshifting effect. To be able to identify galaxies at the highest redshifts (and thus near the beginning of the universe), it is necessary to be able to measure the fluxes of sources at near-infrared wavelengths (>1000 nm). High-redshift galaxies are frequently found by noting a significant break in the spectrum as seen through a set of discrete filters (shown here in terms of their wavelength sensitivities as a set of colored lines). Download the movie: hst_filters_sed_v2.mp4 (with annotations 13MB) or hst_filters_sed_v1.mp4 (without annotations 4.2MB).
Data Releases

Highlights of the Hubble Legacy Fields (HLF) V2.0 Release
- Includes essentially all ultraviolet, optical and infrared data taken by Hubble over 16 years across the Extended CDF-South region including the GOODS-South, HUDF, CANDELS, ERS, HUDF09/12, UVUDF, HDUV and many other programs.
- The largest High Level Science Product (HLSP) data release to date, incorporating 7491 individual HST exposures, totaling 6.4 Msec.
- All images use a coordinate grid tied to the Gaia DR2 reference frame; we also provide results on the original GOODS-S coordinate system.
- The WFC3/UV dataset includes data from the 2009 ERS program which has never been released as a HLSP.
- The ACS/WFC and WFC3/IR data have also been organized and made available as separate data products for twelve one year epochs (from 2002-2007 and from 2009- 2016) as separate data products.
- A photometric catalog is provided for eachof the 13 HST bandpasses used in the HLF dataset.
- The HLF dataset includes 5 deep regions, the original HUDF (now as the XDF dataset) and four newer regions (HLF-HUDF parallels) that are strikingly deep in subsets of the 13 filters.
The release combines exposures from Hubble's two main workhorse cameras, the Advanced Camera for Surveys Wide Field Channel (ACS/WFC) and the Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3), including data from both the infraRed channel (WFC3/IR) and the UV/visible channel (WFC3/UVIS). These data were taken over more than a decade between mid-2002 to the end of 2016. The HLF includes essentially all the near-uv (WFC3/UV F225W, F275W, F336W), optical (ACS/WFC F435W, F606W, F775W, F814W and F850LP filters) and infrared (WFC3/IR F098M, F105W, F125W, F140W and F160W filters) filters. The HLF includes data taken by Hubble over the original CDF-South region including the GOODS-South, CANDELS, ERS, the Extended CDF-S (ECDF-S), numerous SNe followup programs, and many other programs. Given that this dataset combines all images in the archive on the ECDF-S to date from numerous different programs, the HST AR-13252 proposal identified the product under a single global name "Hubble Legacy Field".
more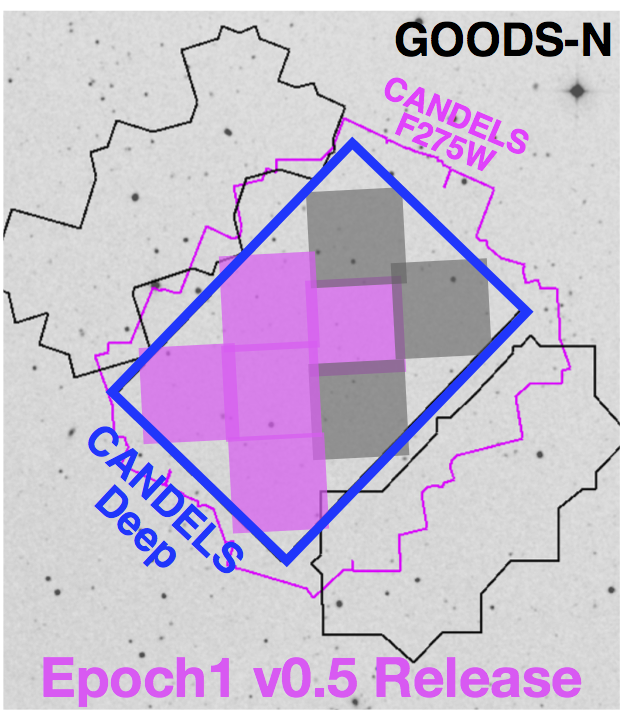
Hubble Deep UV (HDUV) Legacy Survey
The HDUV is a legacy program using the Hubble Space Telescope to obtain deep UV images of the central parts of the two GOODS fields, which was approved in HST Cycle 22. Our program will build on existing WFC3/UVIS data to obtain deep images at 250-350 nm (in F275W and F336W). These data will provide the first complete census of low-luminosity star-forming galaxies at z~0.5-2 and enable a wealth of research by the community. This includes measuring the physical properties of sub-L* galaxies, and characterizing resolved stellar populations to decipher the build-up of the Hubble sequence from sub-galactic clumps.
To ensure these legacy data are fully exploited, we are releasing high-level science data products to the community. The first epoch v0.5 reduced data are already available on our Data Products page!
more
The eXtreme Deep Field (XDF) Data Release v1.0
The XDF is the deepest image of the sky taken with Hubble for searching for the earliest galaxies. It includes ALL images taken by Hubble on the small patch of sky first imaged as the Hubble Ultra-Deep Field (HUDF) and subsequently as the HUDF09 and HUDF12. The XDF also adds images that overlapped the HUDF from many other programs including CANDELS, supernova searches and many others (19 in total). These images were taken over a decade from mid-2002 through to early 2013. The XDF is an exposure of 2 million seconds total from Hubble's two premier cameras, the Advanced Camera (ACS) and the Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3). It consists of 2963 separate images from the ACS and WFC3/IR. ACS flew on the Shuttle to Hubble in 2002 on servicing mission SM3B, while the Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3) flew to Hubble in 2009 on the final Hubble Shuttle mission (SM4).
more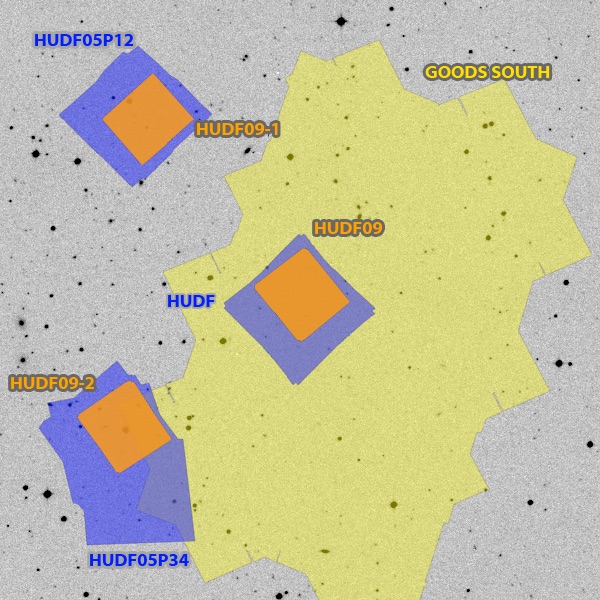
HUDF09 Data Release v1.0
The Hubble Ultra Deep Field 2009 (HUDF09) program observations obtained by HST program 11563 (PI: Garth Illingworth) in Cycle 17 has made publicly available. The program uses WFC3/IR as the prime instrument for 192 orbits to image the deep ACS fields that were obtained in the original HUDF (PI: Steven Beckwith) program and in the HUDF05 (PI: Massimo Stiavelli) program. We have released the data products for this program as an HST High Level Science Product.
more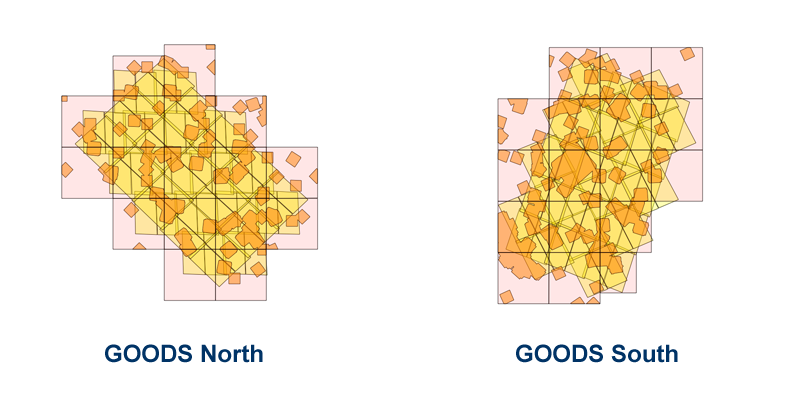
GOODS NICMOS Archival Data
As a part of the HST 10937 (Archival Research) proposal titled Probing the Galaxy Population at z~7-10 Using Archival ACS & NICMOS data PI Rychard Bouwens and colleagues retrieved and process nearly all NICMOS camera 3 F110W and F160W data taken over the GOODS North and South fields.
moreData Reduction Software
HLFRED
HLFRED is a data reduction package for reducing images from Hubble's ACS (WFC) and WFC3 (IR & UVIS) cameras. It is has the capabilities to produce mosaic images from numerous data sets covering a large field. HLFRED was used to create the huge mosaic images for the Hubble Legacy Fields project.
moreNICRED
NICRED is an automatic image processing pipeline for data taken with the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) instrument on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The pipeline currently supports imaging data from camera 2 and 3 and is written in Python and C making it portable across many platforms. The automated processing steps include basic calibration (removing the instrumental signature), cosmic-ray removal, treatment for post-SAA cosmic ray persistence and electronic ghosts (a.k.a. the "Mr. Staypuft" effect), sky subtraction, non-linear count-rate correction, artifact masking, robust alignment and registration for large mosaics, weight map generation, and drizzling onto a final image mosaic. NICRED can combined data across different HST observations, visits and proposals with the need for any pre-defined associations. NICRED creates image products with a signal-to-noise ratio that matches the most careful step-by-step manual NICMOS reductions.
moreAPSIS
Apsis in an automatic image processing pipeline for the Hubble Space Telescope's Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS) instrument. The pipeline supports processing of images from the HRC and WFC cameras on the ACS instrument and is written in Python. The processing steps include empirical determination of image offsets and rotation, cosmic ray rejection, image combination using the drizzle routine called via the STScI Pyraf package, object detection and photometry using SExtractor.
more